
Bluetick Coonhound Breed description: Character & Co
Bluetick Coonhound
Facts & Origin
His job is to shoo raccoons up trees. Raccoon or Coon for short -> Name.
About the breed Bluetick Coonhound
The Bluetick Coonhound is not recognized by the FCI, but UHC and the AKC. In Germany this breed is very rare.
Origin: Louisiana
The Bluetick Coonhound comes from the USA, from Louisiana. It was bred there specifically for the raccoon hunt by crossing English Coonhounds, Foxhounds, French hounds and suitable hybrids with each other.
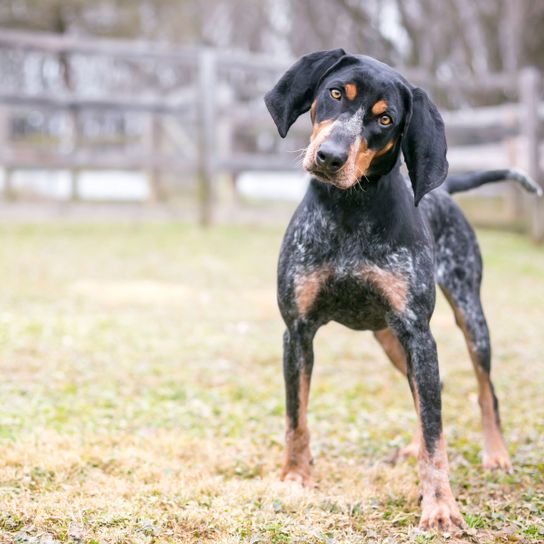

| Alternate Name | - |
| Origin | USA |
| Life expectancy | 11 - 12 years |
| Care requirements | low-maintenance |
| Activity level | high |
| FCI group | not recognised |
| AKC group | Hound Group |
| KC group | not recognised |
Attitude, character and temperament of the breed
The nature of the Bluetick Coonhound: freedom-loving and self-confident.
The Bluetick Coonhound is close to nature, freedom-loving and robust. Its hunting instinct is strongly developed. Since he has a tendency to run off, he must be kept in a securely fenced area.
Because of its strong urge to exercise, it needs plenty of walks and other opportunities to let off steam - whether it's hunting, competing, or playing dog sports.
The Bluetick Coonhound is friendly and always eager to please his human. It enjoys new challenges and loves to learn.
It is self-confident and does not get nervous easily.
Education: not for beginners
Since the Bluetick Coonhound is very self-confident, it is only easy to train if the order of precedence is clear. It will not take an insecure or inconsistent person seriously and will make its own decisions. Therefore the Bluetick Coonhound is not well suited for beginners. On the other hand, it is eager to learn and eager to learn, which again makes training easier. It should be socialized early and get to know both strange people and dogs, then there will be few problems in living together.
Attitude
The Bluetick Coonhound needs enough space to move around, to sniff - and enough boundary not to go running. A large yard with a high fence is perfect.
Use
This intelligent hunting dog is versatile:
- For the raccoon hunt the Bluetick Coonhound was bred, there lies in some areas of America still his main area of use.
- In addition, he is used in many places for fox hunting.
- The Bluetick Coonhound is suitable for various dog sports such as agility, tracking work and the like.
- Also as a companion dog he makes a good figure, but in this case you should keep an eye on his hunting instinct.
Character
Usage

Health and breeding information
Health
As with many larger dog breeds, HD and gastric torsion are recurrent in the Bluetick Coonhound. Patellar luxations are also common.
As with other breeds with droopy ears, the ears are at risk for infection and fungal disease.
Bite or other injuries can occur during hunting.
The dog lives to be 11 to 12 years old.
Care: unproblematic
The care of the Bluetick Coonhound is unproblematic. The coat must be brushed from time to time.
The hanging ears should be checked and cleaned regularly to prevent infections. Also, as with any other breed of dog, you should check the paws, claws and eyes regularly.
You can either brush their teeth regularly with a dog toothbrush or achieve the same effect with chewing snacks.
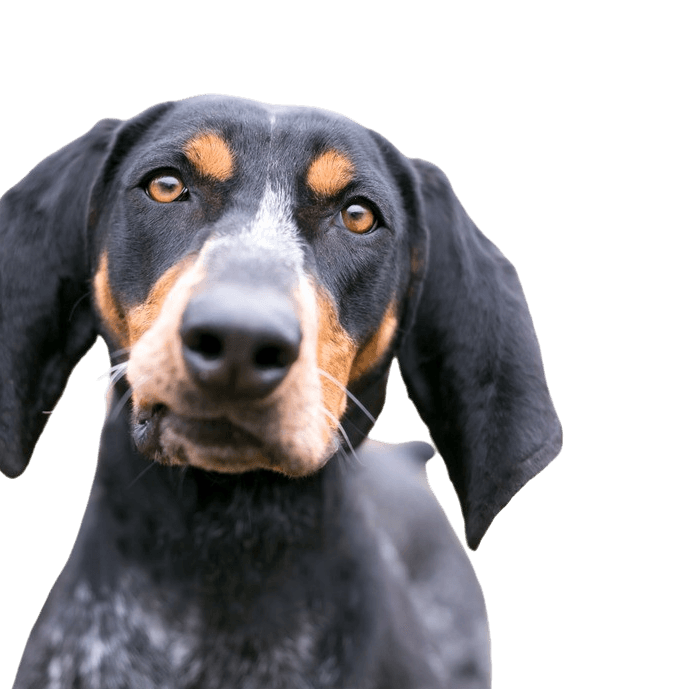


The exterior of the blue Coonhound: coat with blue tinge and spots.
Males grow to a height of 56 to 69 cm, bitches 53 to 64 cm.
Males reach a weight of 25 to 36 kg, bitches from 20 to 29 kg.
The coat has a very unique colouring in white-blue with black speckles and spots. On the head it is black, sandy and brown.
The dog is strongly and massively built.
The bark of the Bluetick Coonhound is very characteristic and rather reminds of a howl.
| Fur length | short |
| Fur | flat coated |
| Ear shape | Floppy Ear |
| Tail | lang |
| Anatomy | rugged |
| Size ♀ | 53 - 64 cm |
| Weight ♀ | 20 - 29 kg |
| Size ♂ | 56 - 69 cm |
| Weight ♂ | 25 - 36 kg |
| Suitable For | - |
Colors

Known Diseases
Hip dysplasia (HD)
The hip dysplasia or hip joint dysplasia of the dog (HD) is a maldevelopment of the hip joint.
Gastric torsion
Gastric torsion is a disease in which the stomach rotates around its own longitudinal axis. The cause of the disease is not known.
Patellar luxation
Patellar luxation is the term used to describe a displacement of the kneecap, which is one of the most common causes of lameness in dogs.
Other large dogs
Useful Articles
You can find articles that might interest you in the dogbible blog to match your favorite breed.
Visit our magazineto stay up to date on dog trends.
To find out more, view our Privacy Policy
Find here the breed that suits you and find out what character traits it has. Here you can also learn more about the origin, size and weight of your favorite breeds.
Matching your favorite breed, you'll find articles that might interest you on the dogbible dog blog.
Silver Labrador - buying, breeders and information
Driving with a dog - Tips for a Dog-Mobile






















