
Norfolk Terrier Breed description: Character & Co
Norfolk Terrier
Facts & Origin
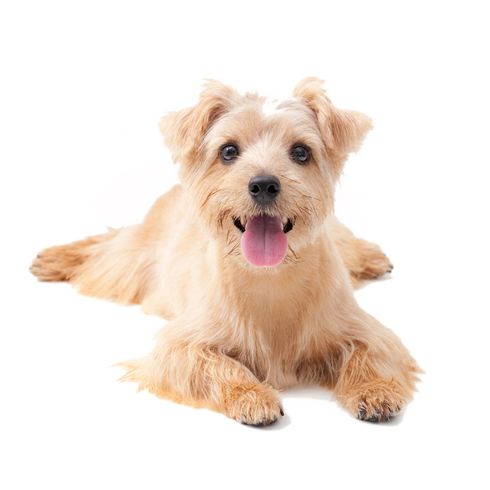
The Norfolk Terrier is a particularly spirited handbag-sized pet. It is one of the smallest terriers.
What is the origin of Norfolk Terriers?
During the 19th century, terriers were bred in Britain to control rats and rabbits. From 1818 onwards, various other terrier breeds were crossed in. The wiry terriers accompanied hunters on small game hunts. They shooed foxes and other animals from their dens. Before being used, the dogs could be carried comfortably on horseback. The Norfolk Terrier started its triumphal procession as a companion dog. In 1932 the Norwich Terrier Club was founded, in which dogs with standing ears and tipped ears were represented. In order to avoid an unattractive appearance, the two varieties were not bred to each other. Only in 1964 the separation into two breeds took place:
-
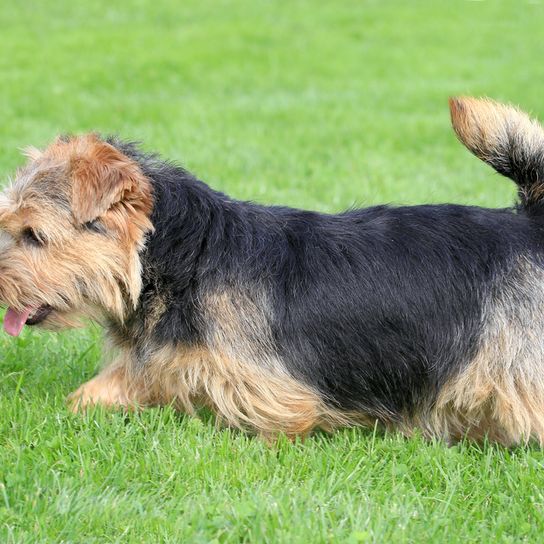
Norwich Terrier: prick ears
-
Norfolk Terrier: tipped ears
Today the dog breed is listed by the FCI under standard number 272, in group 3, section 2.




| Alternate Name | - |
| Origin | UK |
| Life expectancy | 10 - 15 years |
| Care requirements | high-maintenance |
| Activity level | high |
| FCI group | Small sized Terriers |
| AKC group | Terrier Group |
| KC group | Terrier Group |
Attitude, character and temperament of the breed
What are typical character traits of Norfolk Terriers?
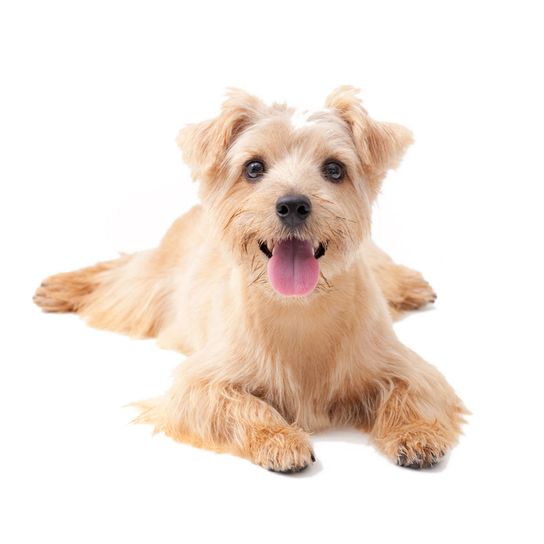
The Norfolk Terrier is bright and lively. It has a strong character and great self-confidence. The small dog is very independent and also likes to overestimate itself. It likes to assert its own head. Therefore, loving consistency is especially important in its upbringing. The loyal dog is closely tied to its family. The dog loves children and likes to play with them. It vigilantly repels threats with energetic, fearless barking. The amiable terrier should be accustomed to other animals at an early age so that living together goes smoothly. As a pack dog, the Norfolk Terrier enjoys the company of other animals. As a companion dog it is uncomplicated to keep. It adapts easily to different housing conditions and can be kept both in the city and in the country. Long walks and dog sports keep its physically and mentally occupied.
Character
Usage


Health and breeding information
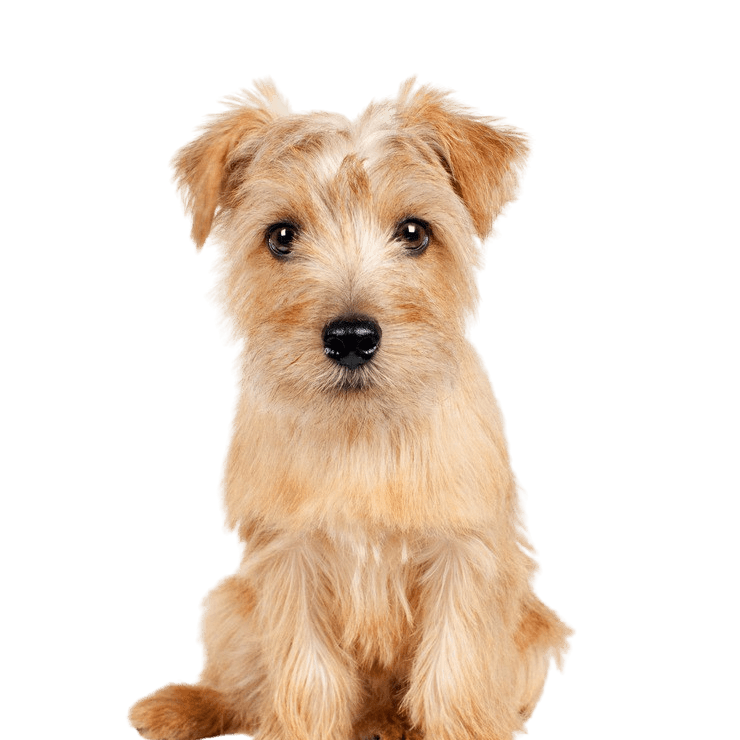
What are typical diseases of Norfolk Terriers?
Although the dog has a robust health, some hereditary diseases occur
- Patellar luxation
- Hip dysplasia
- heart disease: the mitral valves do not function
- Epilepsy
Norfolk Terrier breeding - where, how, what?
To get a healthy Norfolk Terrier puppy, you should buy the dog from a breeder:
As there are only a few litters, the waiting time is often very long. As an alternative you can adopt a Norfolk Terrier:
- Rescue Me Norfolk Terrier Directory
- Norfolk Terrier Rescue Contacts


What are the breed characteristics of Norfolk Terriers?
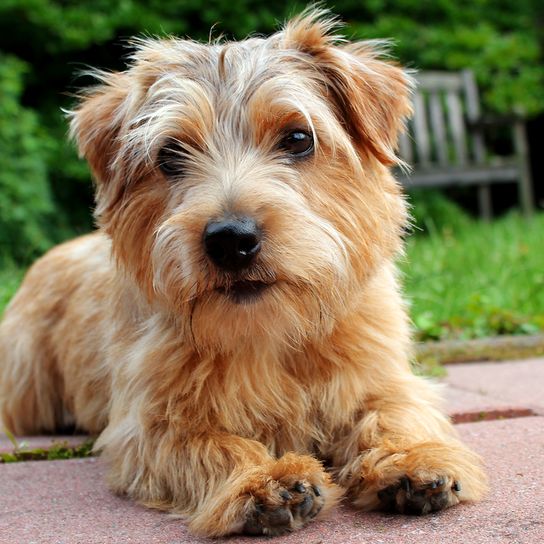
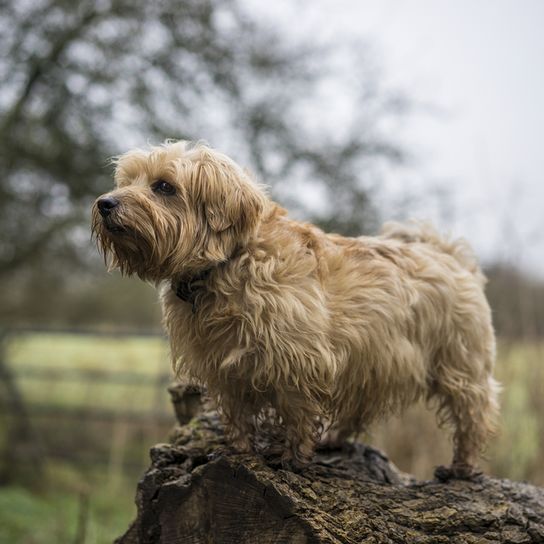
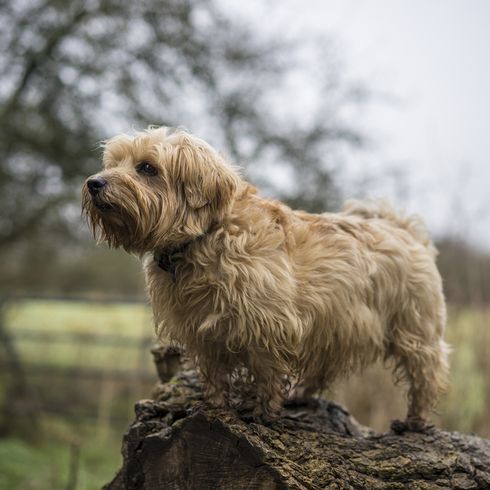
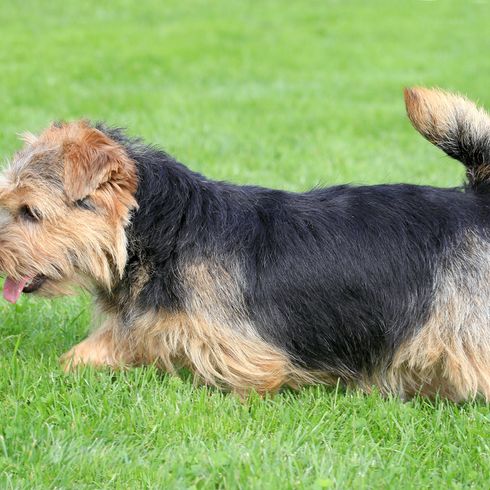
The short-legged terrier has firm bones and a compact body. The V-shaped ears are folded forward and lie close to the cheeks. The skull is broad with a pronounced nasal stop. The long tail is carried horizontally. Today the tail may no longer be docked.
Appearance and coat of the Norfolk Terrier
The Norfolk Terrier has a dense undercoat and hard, wiry topcoat that lies close to the body. The coat is weather resistant and protects the small dog from cold and wet conditions. In the area of the head the fur hairs are softer and shorter. The eyebrows are bushy. The muzzle is framed by a dense beard.
Coat colours:
- wheaten
- grizzle
- black with tan
- red
Since the coat is not changed, it must be trimmed three times a year to remove loose hair.
How big does a Norfolk Terrier grow?
Male: 24 to 25 cm
bitch: 23 to 24cm
How much does a Norfolk Terrier weigh?
-
Male: 6 to 7 kg
-
bitch: 5 to 5,4 kg
How old does a Norfolk Terrier get?
Norfolk Terriers can grow older than 15 years.
| Fur length | medium |
| Fur | rough-haired |
| Ear shape | Tilt-ear |
| Tail | short |
| Anatomy | strong |
| Size ♀ | 23 - 24 cm |
| Weight ♀ | 5 - 5 kg |
| Size ♂ | 24 - 25 cm |
| Weight ♂ | 6 - 7 kg |
| Suitable For | Children |
Colors






Known Diseases
Epilepsy
Definition: Dog has epilepsy if, for example, at least two epileptic seizures occur more than 24 hours apart.
Heart disease
Can occur frequently in dogs and can sometimes be treated with medication.
Hip dysplasia (HD)
The hip dysplasia or hip joint dysplasia of the dog (HD) is a maldevelopment of the hip joint.
Patellar luxation
Patellar luxation is the term used to describe a displacement of the kneecap, which is one of the most common causes of lameness in dogs.
Other small dogs
Useful Articles
You can find articles that might interest you in the dogbible blog to match your favorite breed.
Visit our magazineto stay up to date on dog trends.
To find out more, view our Privacy Policy
Find here the breed that suits you and find out what character traits it has. Here you can also learn more about the origin, size and weight of your favorite breeds.
Matching your favorite breed, you'll find articles that might interest you on the dogbible dog blog.
Driving with a dog - Tips for a Dog-Mobile
Winter hiking with your dog - these 5 tips will help you work as a team






















