
Bullmastiff Breed description: Character & Co
Bullmastiff
Facts & Origin
The Bullmastiff was originally bred as a protection dog for British gamekeepers. Today, they have established a reputation as a well-suited family dog with its advocates. You can make sure that the Bullmastiff's full potential of their generally balanced, people-orientated nature fully develops through early puppy training and consistent, non-violent socialisation.
Origin of the Bullmastiff
The first breeds of Bullmastiff puppies with today's character are known from 19th century England. There, the breed was achieved by crossing the Old English Bulldog with the Old English Mastiff resulting in a well-suited protection dog for the gamekeepers of the Landlord. Outside of English territories the strong, big dog only became known after the middle of the 20th century. Later on, crossbreeding with Bloodhounds further developed the Bullmastiff's scenting ability to add to their already existing protection and guard dog potential.
Breed characteristics of the Bullmastiff
- FCI Standard Bullmastiff (157) Group 2 Pinscher and Schnauzer - Molossoids - Swiss Mountain Dogs; Section 2 Molossoids; 2.1 Great Dane dogs
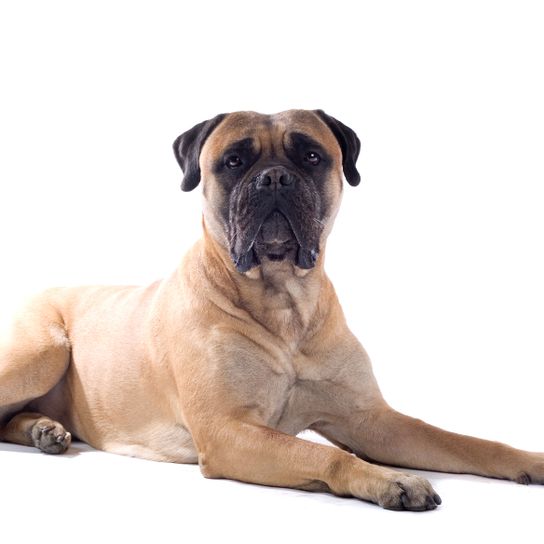
- Appearance: Proud and muscular physique, overall strong build
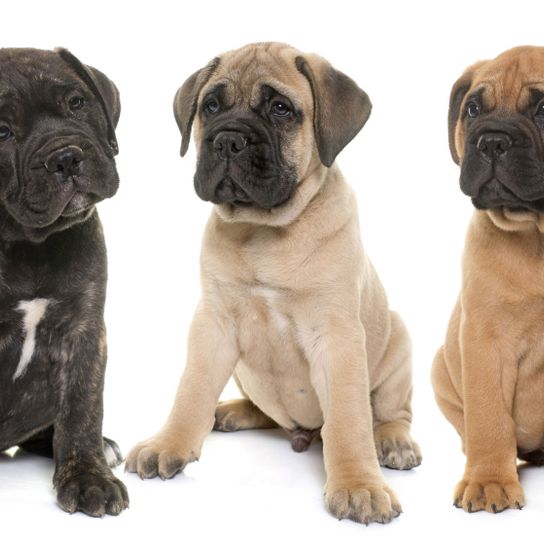
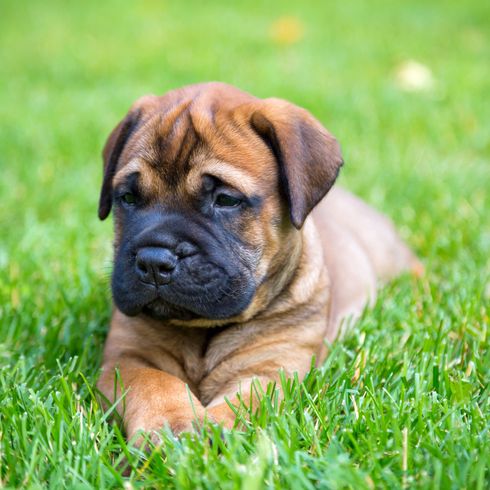
- Breeding types: short coat, hard and smooth in the colours fawn, brindle or red with permitted shading and occasionally a white chest marker
- Other physical characteristics: V-shaped, folded back ears; straight, muscular back on sturdy legs; tail set high - when at rest it is carried almost horizontally or slightly downwards
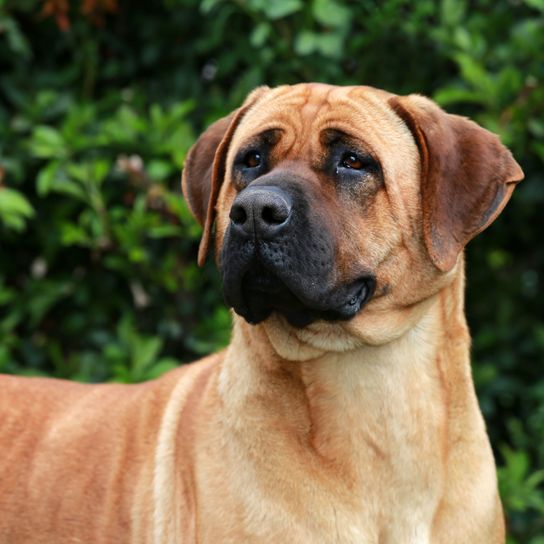
- Square head - appears big in relation to the body
Conditions for the Bullmastiff as a list dog
Despite its high stimulus threshold and good-natured character, the Bullmastiff belongs to the "list of potentially dangerous dogs". These regulations apply in German federal states as well as in German-speaking countries:
- Germany (Berlin): List dog without categorisation
- Germany (Baden-Württemberg, Brandenburg, Bavaria, Hamburg and North Rhine-Westphalia): List dog category 2 (proof of harmlessness by providing a character test is possible)
- Switzerland: In eleven cantons keeping with certificate of competence possible, in Ticino permission necessary, in Geneva purchase, keeping and breeding prohibited
- Austria: In Vienna keeping these dogs is only allowed with a dog handler's license, in Vorarlberg keeping is only possible with a special permission of the mayor
Using the Bullmastiff
Originally, the Bullmastiff was bred to silently track down poachers and keep them free of injury for the gamekeeper's arrest. But with the end of the Landlords, this field of work became obsolete. Now, the British police has discovered the gentle but respectable giants as reliable partners for police service. Their fine sense of smell still makes them a top utility dog for authorities, among other things for tracking purposes. But nowadays, Bullmastiffs are also bought by private individuals. Because of their calm nature, their playful and joyful temperament as well as their unmistakable facial expressions they have become popular even with celebrities in the film world in the last few decades.




| Alternate Name | Mastiff |
| Origin | England |
| Life expectancy | 8 - 10 years |
| Care requirements | low-maintenance |
| Activity level | average |
| FCI group | Molossian type |
| AKC group | working group |
| KC group | working group |
Bullmastiff mixes
Attitude, character and temperament of the breed
Nature of the Bullmastiff
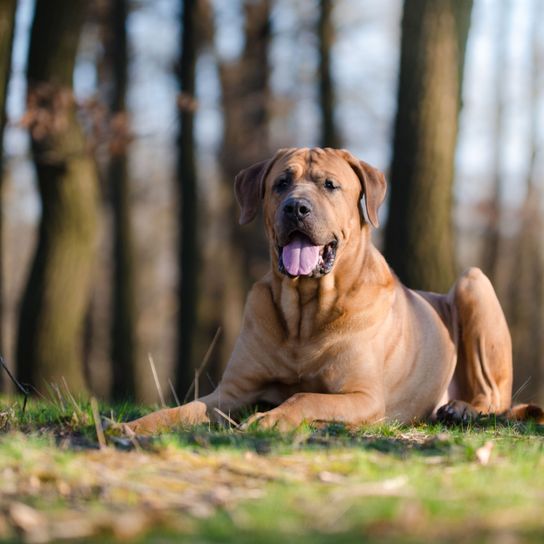
Intelligence, courage and strong family bonds are the three pillars of the reliable Bullmastiff's temperament. But stubbornness and a mind of its own also determine the character of this impressive dog. Therefore, you should train and socialise the puppies in a consistent manner. If this succeeds, you will end up with a calm, adaptable and quiet dog when it is fully grown. An unmistakable characteristic of the Bullmastiff are its facial expressions. Whenever they see something exciting, wrinkles on their forehead appear. If they suspect danger in their family's surroundings, they will alarm you know with a single, deep bark.
Keeping and particularities of the Bullmastiff
Even before you have found your Bullmastiff, it is best to get in contact with your regional dog school. Starting at puppy age, socialising them with other dogs and playful training with humans are the basic requirements for a harmonious life together. Punishments undermine the good-naturedness of the dog rather than promoting it. Instead, with the right reward, they will learn quickly and enthusiastically. Adult Bullmastiffs are affectionate and don't have a hunting instinct. They need to be kept occupied and require consistent behaviour of their owners to ensure their well-being. The short coat is easily groomed with a nubby glove when you spend time petting your dog.
Character
Usage
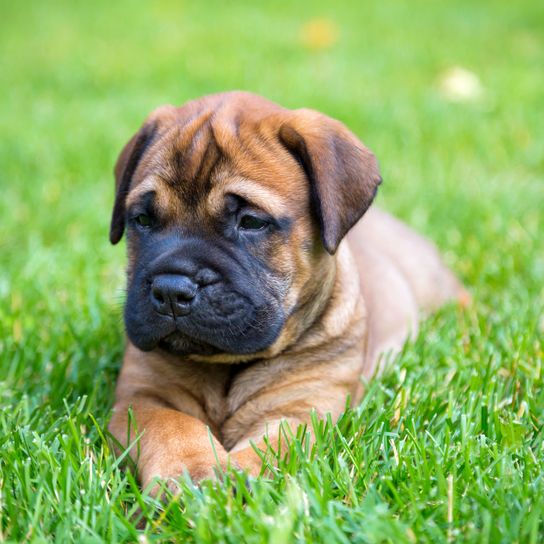


Health and breeding information
Bullmastiff and typical breed diseases
With your Bullmastiff puppy you should have the vet check for a possible higher disposition for developing hip joint dysplasia. Depending on the breed, cancer can develop at an advanced age or the Cavarial-Hyperostosis-Syndrome (an inflammatory disease of the upper skull) can occur. A malposition of the eyelids is rare, but typical for the breed. For now there are effective painkillers available that have been helping dogs alleviate the symptoms of such diseases throughout their lives.
You should pay attention to this with your Bullmastiff breeder
- Already parent animals make the impression of a famously balanced, yet bright Bullmastiff temperament when visiting the dog.
- The breeder does not simply sell, but agrees to a visit at the breeding place without restrictions.
- When you buy a Bullmastiff, the breeder will give you comprehensive papers on the pedigree, veterinary examinations and membership of the association.
- The contact between Bullmastiff puppies, their parents, the family and you as a stranger is noticeably relaxed and comfortable. Playful first contact is a sign for a good basic socialisation.
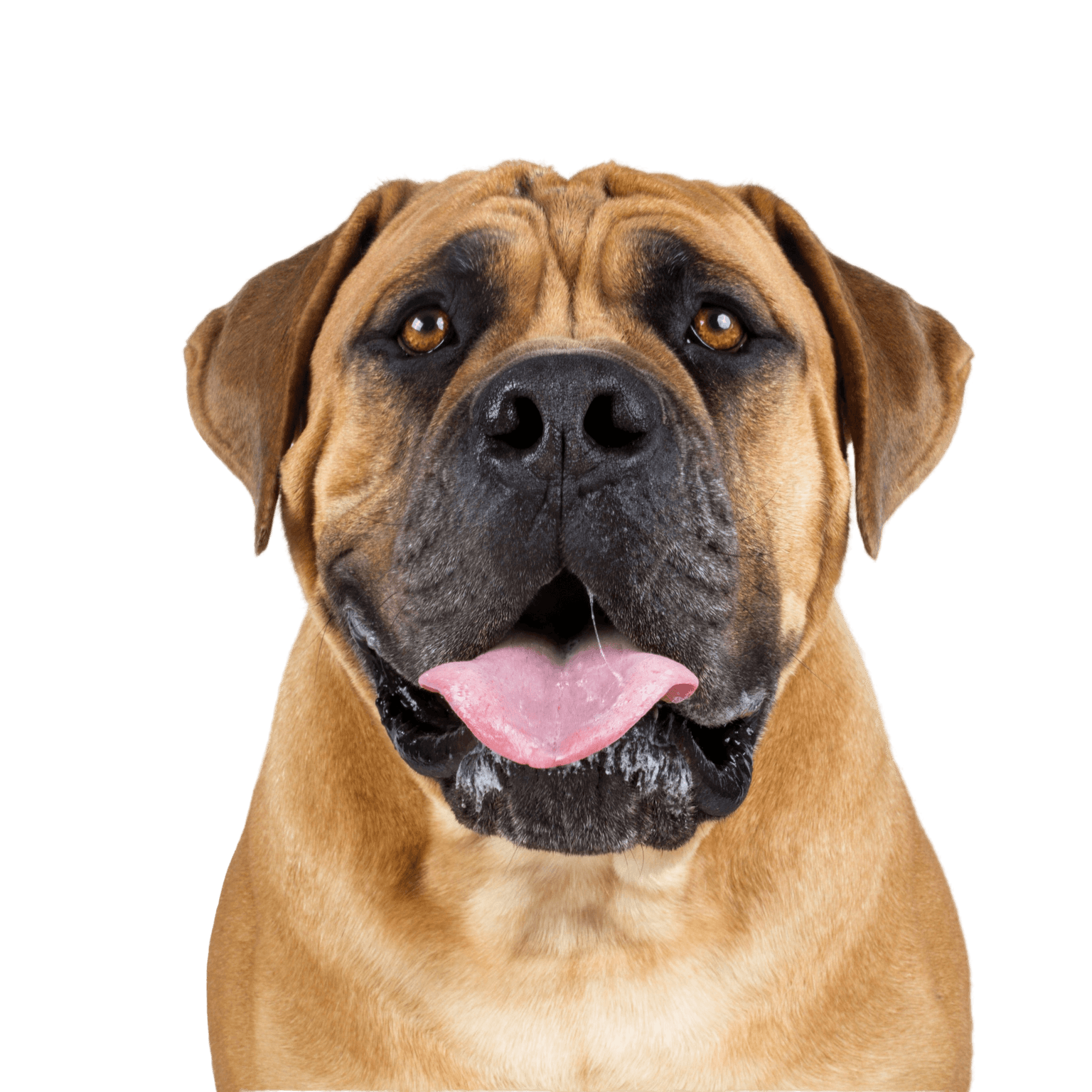


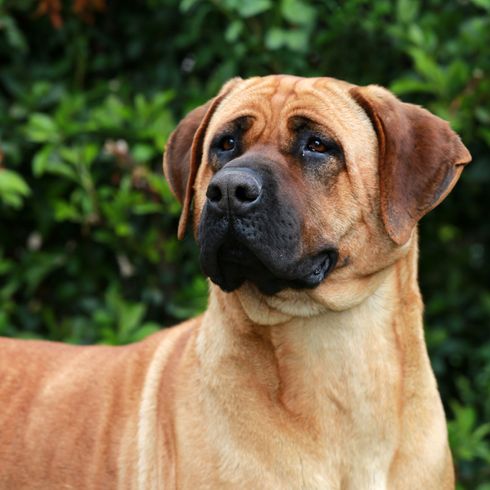
Appearance and coat of the Bullmastiff
The Bullmastiff looks like an unstoppable powerhouse to strangers. According to the original breeding, this was also intended. First poachers and later thieves and delinquents should feel frightened by their sight alone. You should take this potential to make other people feel uneasy into account during walks if you want to buy a Bullmastiff. Nevertheless, a well-behaved dog of this breed comes across as calm and balanced. The dog's coat is short, smooth and hard in the typical shades of the breed. Mask and ears are usually darker than the coat shades on the rest of the body.
Bullmastiff: size, weight and life expectancy
- Size: 61 to 69 centimetres (bitches smaller than males)
- Weight: 41 to 59 kilograms (bitches lighter than males)
- Average age: ten years or more
| Fur length | short |
| Fur | - |
| Ear shape | Floppy Ear |
| Tail | lang |
| Anatomy | square, hefty |
| Size ♀ | 61 - 66 cm |
| Weight ♀ | 45 - 54 kg |
| Size ♂ | 64 - 68 cm |
| Weight ♂ | 50 - 59 kg |
| Suitable For | - |
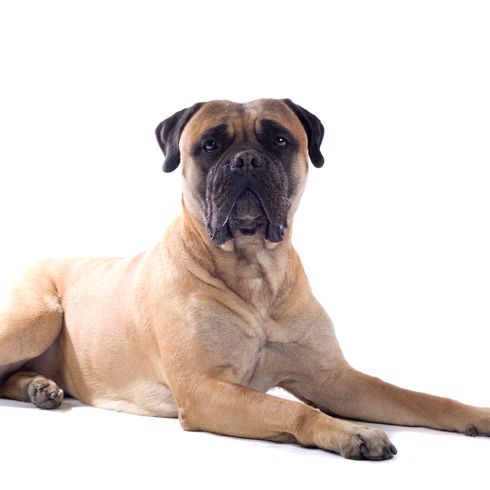
Colors





Known Diseases
Teat Tumors
Tumours of the mammary gland, also known as mammary tumours, are among the most common cancers in dogs.
rolled Eyelid
A rolled eyelid (entropion) is an eyelid malposition in dogs
FAQ
-
Yes, the Bullmastiff is a listed dog and is colloquially known as a fighting dog. It is considered dangerous and is therefore listed in Austria, Germany and Switzerland.
-
Yes, the Bullmastiff is a Molossian breed.
Other large dogs
Useful Articles
You can find articles that might interest you in the dogbible blog to match your favorite breed.
Visit our magazineto stay up to date on dog trends.
To find out more, view our Privacy Policy
Find here the breed that suits you and find out what character traits it has. Here you can also learn more about the origin, size and weight of your favorite breeds.
Matching your favorite breed, you'll find articles that might interest you on the dogbible dog blog.
Allergy dog: Hypoallergenic breeds really exist?
8 emotional movies you should know as a dog fan



























