
Tibetan spaniel Breed description: Character & Co
Tibetan spaniel
Facts & Origin
Ancestry and origin of the Spaniel from Tibet
It is assumed that the breed goes back to dogs that already lived 1,000 years BC in Central Asia. In Europe the dogs were proved for the first time in 1895 in an English breeding. After the 2nd world war the breed was as good as extinct in Europe. After the import of new dogs from Tibet, the breed was rebuilt and recognized by the FCI in 1961. However, the stud books are not kept in the country of origin, Tibet, but exceptionally in England. These smallest of all Tibetan dog breeds still live today as recognized companions of the monks in the monasteries of the Himalayas.




| Alternate Name | Tibetan spaniel |
| Origin | Tibet |
| Life expectancy | 12 - 16 years |
| Care requirements | high-maintenance |
| Activity level | average |
| FCI group | Tibetan breeds |
| AKC group | non-sporting group |
| KC group | utility group |
Attitude, character and temperament of the breed
Breed characteristics and temperament
The Tibetan Spaniel is listed in the FCI system in Group 9 (Companion and Society Dogs), Sec. 5 (Tibetan Dog Breeds), Standard No. 231, without working test. The following characteristics distinguish the Tibetan Spaniel:
- Intelligence
- courage
- fearlessness
- liveliness
- Loyalty
These affectionate dogs love to get comfortable on their owners' laps. Although it seeks closeness with its master or mistress, however, the Tibetan Spaniel will never be submissive. The dogs are also naturally very wary and suspicious of strangers.
Keeping and raising a Tibetan Spaniel
These fun little dogs can be kept in any city apartment. They are exceptionally friendly family dogs, with a certain tendency to be stubborn and headstrong. Therefore a consistent education is important. However, the dogs do not react to pressure or coercion. They regard themselves as equal partners of their owners. Then, however, they are uncomplicated companion dogs, full of urge to move, who love long walks. To a certain extent Tibetan Spaniels are even suitable for allergy sufferers.
Character
Usage


Health and breeding information
Care and nutrition
Tibetan Spaniels have a low maintenance coat. However, to avoid fungus buildup, their coats should be combed or brushed at least once a week (more frequently during coat changes). The dogs' hanging ears are prone to inflammation and should be checked weekly and cleaned if necessary. Tartar prophylaxis by regular brushing with a special dog toothbrush and toothpaste is also advisable. For a healthy diet, value should be placed on high-quality food with a high proportion of meat. Dry chews also support dental hygiene. Since Tibetan Spaniels are small dogs with low energy requirements, their weight must be monitored regularly to avoid disease-promoting obesity.
Health and life expectancy
Tibetan Spaniels are naturally very robust and healthy dogs. However, the dogs are prone to progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) due to hereditary disposition. This is an eye disease in which the retina slowly dies. The result is almost always complete blindness. However, there is a genetic test which makes it possible to exclude the disease as far as possible by appropriate selection in breeding. The breed is also relatively insensitive to weather conditions. Both cold in winter and heat in summer are well tolerated. With appropriate husbandry and care they can reach an average age of 13 to 16 years.
Things to know
If you want to buy a Tibetan Spaniel, no matter if adult or puppy, you should contact a breeder who is affiliated to a club. You can get a list of breeders at theInternational Club for Tibetan Dog Breeds e.V..
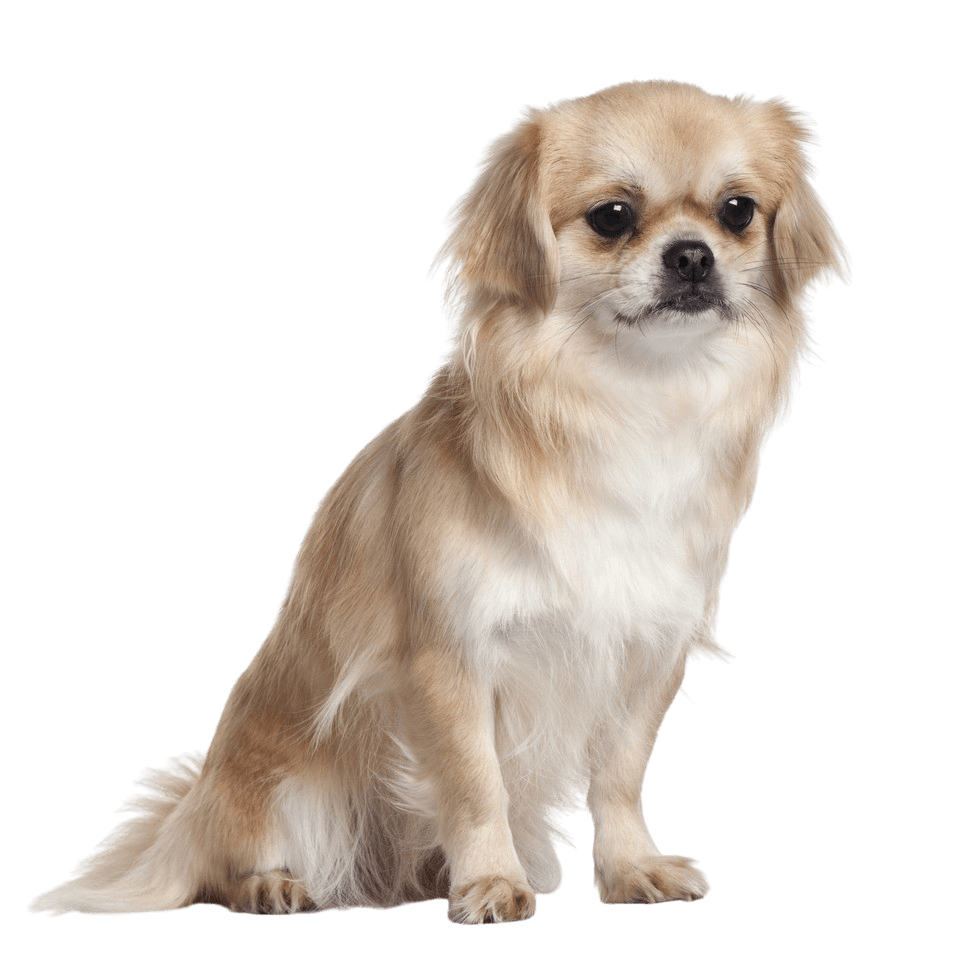


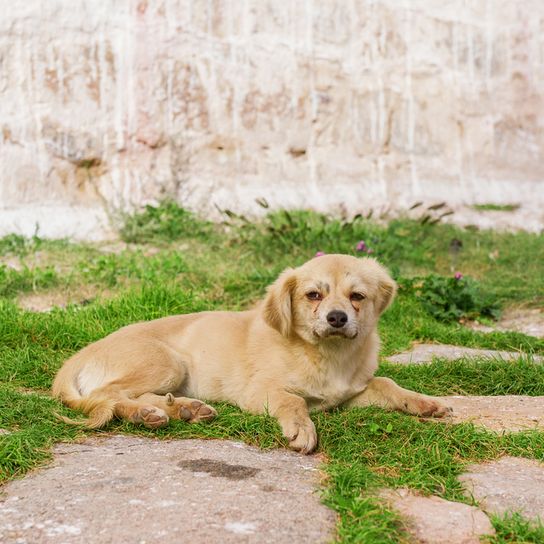
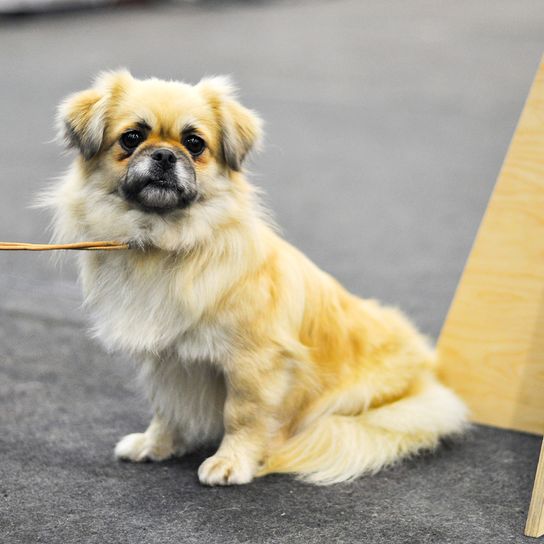
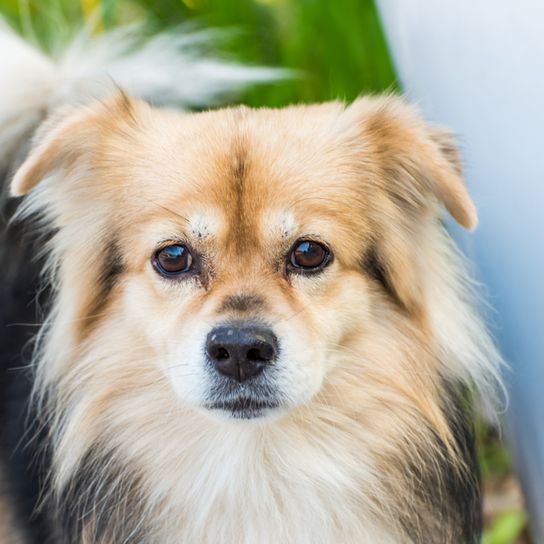
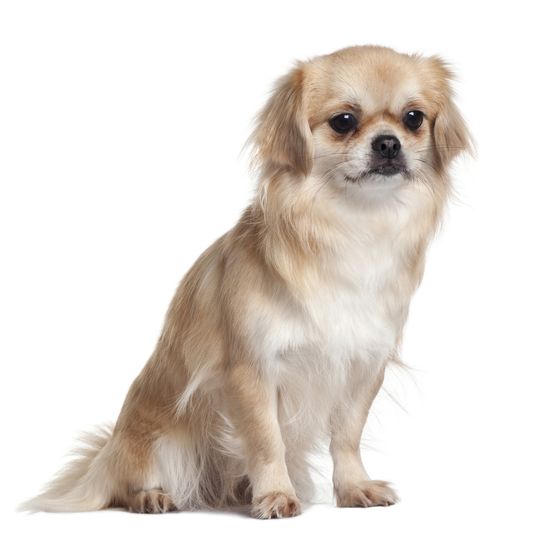
Breed characteristics and appearance of the Tibetan Spaniel
The dogs have hardly changed their appearance in the course of the centuries. With a withers height of the males of 25.4 cm (bitches are slightly smaller) and a weight of 4 to about 7 kg, the breed comes in almost all coat colors. No matter if golden, cream, red, grey-brown, black and tan or black, only brown (liver colour) is not allowed in breeding.
| Fur length | long |
| Fur | flat coated |
| Ear shape | Tilt-ear |
| Tail | fanned out |
| Anatomy | square |
| Size ♀ | 20 - 24 cm |
| Weight ♀ | 4 - 6 kg |
| Size ♂ | 20 - 25 cm |
| Weight ♂ | 4 - 7 kg |
| Suitable For | Beginner, Children, Seniors |
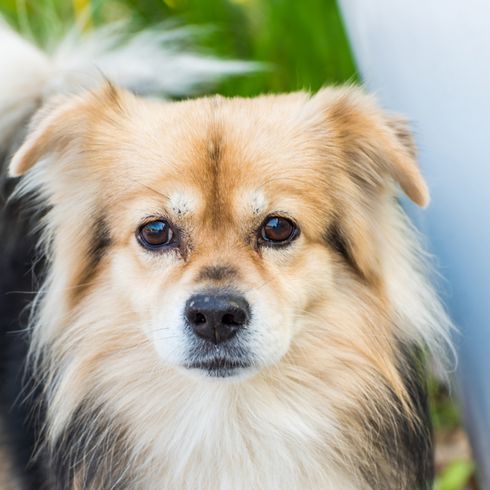
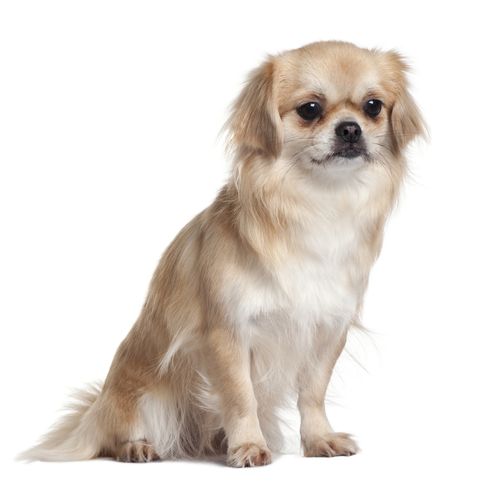
Colors








Known Diseases
Progressive Retinal Atrophy (PRA)
Progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) is a slowly progressive death of the retina in dogs.
Other small dogs
Useful Articles
You can find articles that might interest you in the dogbible blog to match your favorite breed.
Visit our magazineto stay up to date on dog trends.
To find out more, view our Privacy Policy
Find here the breed that suits you and find out what character traits it has. Here you can also learn more about the origin, size and weight of your favorite breeds.
Matching your favorite breed, you'll find articles that might interest you on the dogbible dog blog.
Vacation with the dog at the sea: Is salt water dangerous for my treasure?
This genius hack to trim your dog’s nails and more tips
MDR1 mutation - everything you need to know about it if you have a dog






















